AI Applications in Healthcare: From Drug Discovery to Patient Care
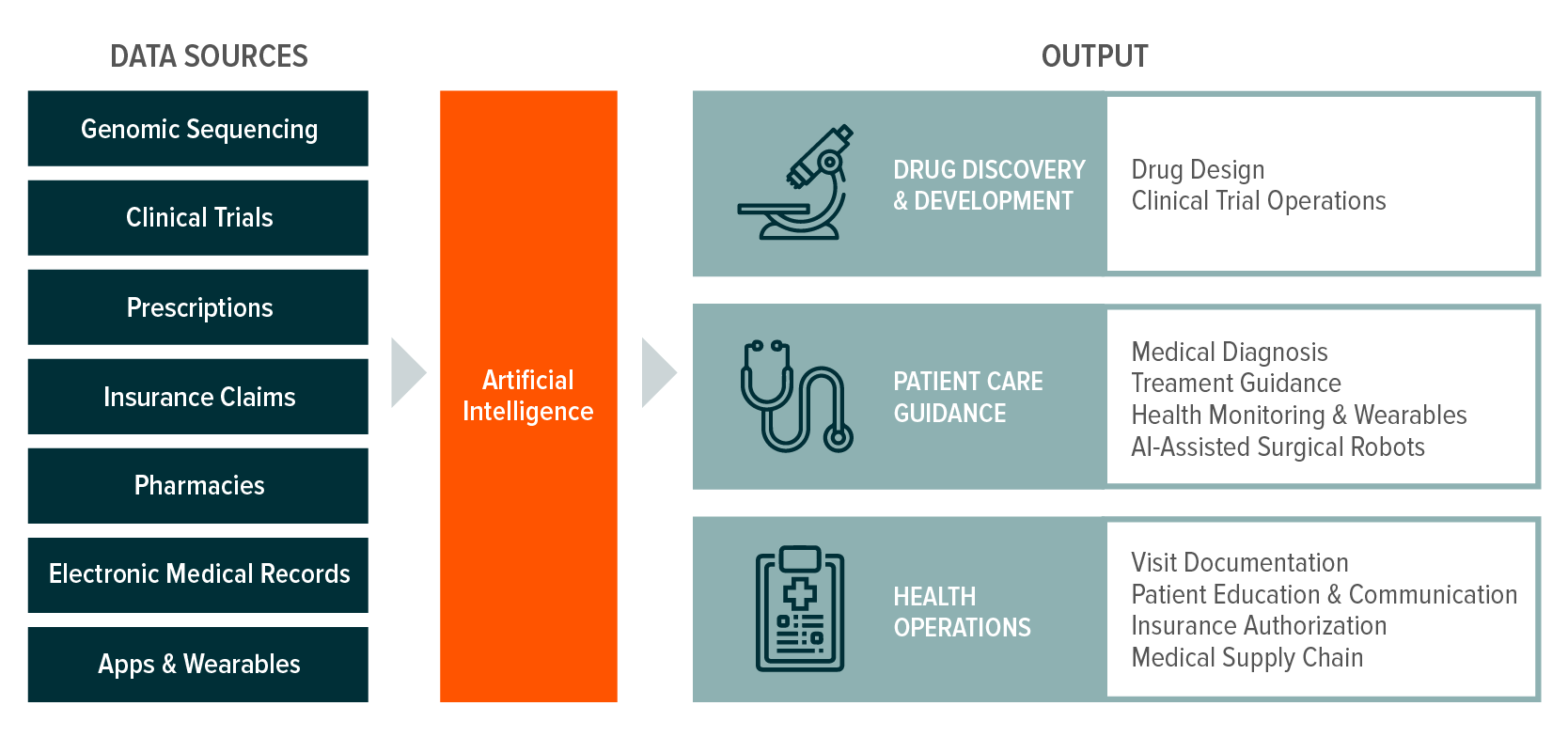
We believe the healthcare system is at a turning point, leveraging digital health technologies to render longstanding inefficiencies in healthcare a thing of the past. Artificial intelligence stands at the heart of this transformation, with the potential to improve medical outcomes by 30-40% while saving the United States as much as 10% of annual healthcare spending.1,2
Key Takeaways
- Drug discovery is a long and expensive process with many inefficiencies and potential pitfalls. AI has the potential to help in virtually every step of the process, from early-stage computer simulations to late-stage trial design, patient recruitment, and data analysis.
- The healthcare industry is large and complex, with a multitude of insurers and providers. This creates frictions, inefficiencies, and clerical work that AI is poised to help reduce, potentially saving significant time and money.
- Given the size and diversity of the healthcare sector, picking individual winners from AI’s disruption of the industry can be challenging. Consequently, ETFs that offer broader exposure to this megatrend may be an appealing option for investors.
AI in Drug Development
Drug discovery is a notably difficult process. Despite technological advancements, developing a new medicine still takes 10-15 years and costs US$1.3 billion on average.3, 4 Also, 90% of investigational drugs fail when tested in humans due to having no effect or too many side effects.5 Complicating matters, clinical trials are notoriously difficult to design and operate, often impeding the approval of treatments.
AI in Drug Discovery: Supercharging Decades of Computer-Aided Drug Design
Computer simulation software has been used to develop investigational drugs since the 1990s, successfully reducing costs and increasing success rates in drug discovery.6 New AI-enabled models, however, propose even more favourable unit economics. By running millions of scenarios, AI software can reduce the cost of preclinical drug development by 20-40% and accelerate design and validation of drug candidates by as much as 15x.7, 8
To drug development, AI offers:
- Better Molecule Construction: AI software predicts the 3D structure of target proteins, drug protein interactions, and activity in new therapies. Improved molecule construction can help ensure high levels of efficacy from investigational drugs in preclinical studies. Most importantly, however, AI can help ensure the greatest correlation between pre-clinical studies in mice and late-stage in-human trials.
- Maximised Investigational Efforts: AI software helps design multi-target drug molecules and predict drug repurposing to maximise a treatment’s reach. With a single molecule, new treatment categories like GLP-1s (glucagon-like peptide 1) have shown success across type 2 diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular illness, and beyond. AI can help predict whether a treatment for one condition might also be useful for other diseases, which could make it easier to identify blockbuster treatments early in the drug discovery stage.
- Enhanced Patient Identification: AI software predicts toxicity and efficacy of treatments via genomic profiling, helping identify characteristics of patients that could benefit. Setting these guidelines early in the drug development process can help clearly outline clinical trial participants and increase the likelihood for success of investigational drugs. Once approved, it also carves a clear path for treatment marketing.
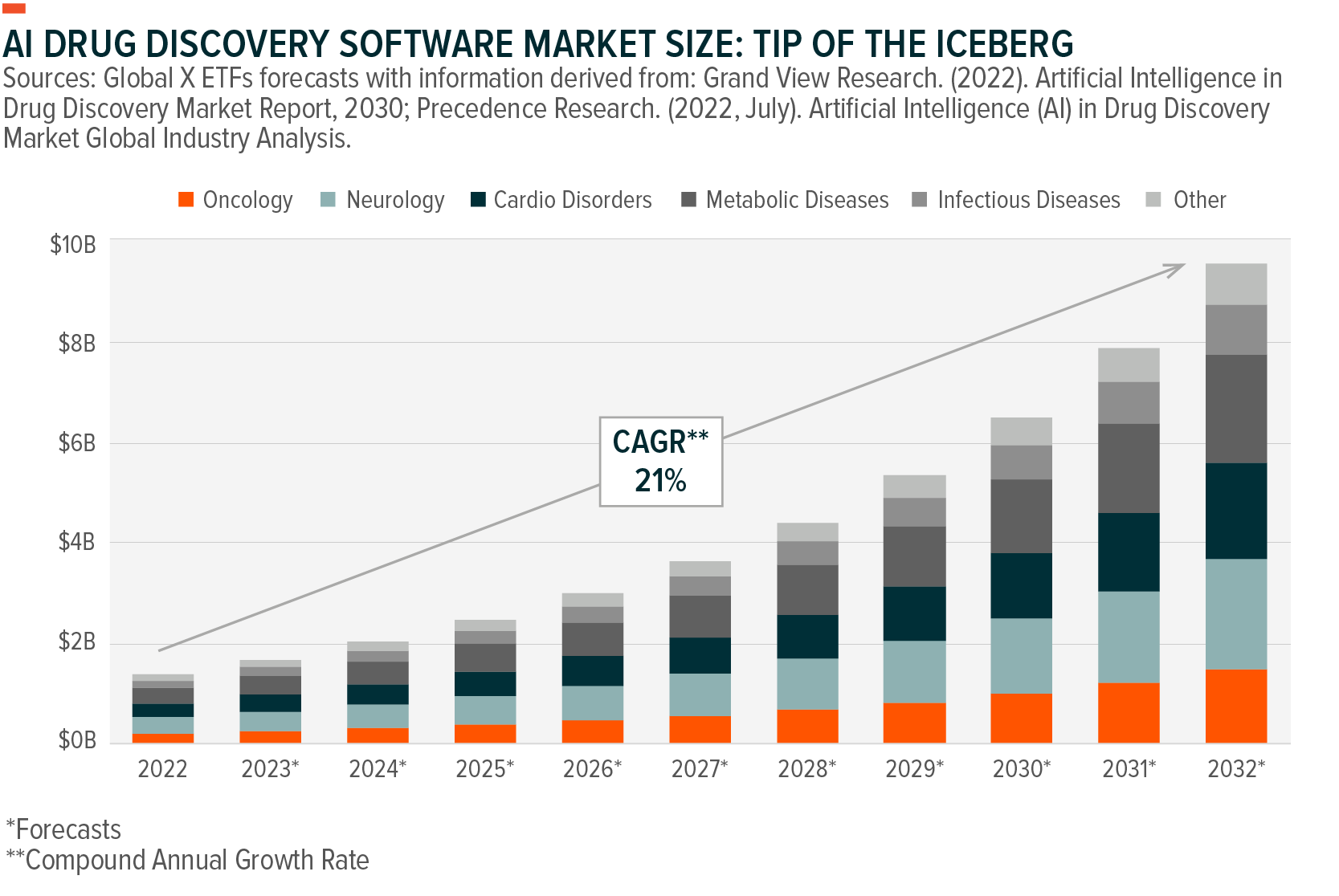
The impact of broader AI drug discovery is sizable and has the potential to change the drug discovery process as we know it. An estimated 30% of new drugs are expected to be discovered using AI technology by 2025, up from zero today.9 An increased use of AI drug discovery is expected to, in turn, lead to an additional 50 novel therapies over a ten-year period, which alone could translate to over US$50 billion in revenues.10
AI in Clinical Trial Operations: Modernising In-Human Trials
Designing and conducting clinical trials is known for its inherent complexity and challenges. Artificial intelligence can reduce operating costs of clinical trials and offers a scalable solution for some of the biggest stumbling blocks in the drug development process.
- Trial Design: The causes of a negative trial outcome can be difficult to discern, as unknown flaws in trial design can mask the true efficacy of a drug. AI can identify patterns that humans can’t from trial results, helping determine if, for example, a drug is only a good fit for a specific subsect of patients.
- Ineffective Recruitment: An estimated 86% of trials miss their enrolment deadlines due, in part, to 85% of patients being unaware that there is a clinical trial they could participate in.11 Nearly a third of phase III trials fail due to enrolment difficulties, such as trouble identifying the right patients or issues with retention of participants.12 By analysing large datasets of patient records to identify eligible candidates for clinical trials, AI helps reduce the time and cost of recruiting participants. Tempus, an AI precision medicine company, accelerates clinical trial enrolment by achieving trial activation within ten business days, a steep improvement from the industry average of eight months.13 AI is projected to save US$13 billion on clinical trial participant identification.14
- Insufficient Data: Each investigational treatment uses a rubric to evaluate its efficacy. For some illnesses, we rely on surrogate endpoints, which measure the effect of the treatment that may correlate to clinical improvement but do not necessarily have a guaranteed relationship. An estimated 80% of cancer treatment trials rely on surrogate endpoints.15 AI-powered wearables can help measure drug efficacy and monitor patients during clinical trials, potentially eliminating the need for frequent visits to testing centres. Increased integration with electronic patient-recorded data and telemedicine are expected to make AI models even more powerful.
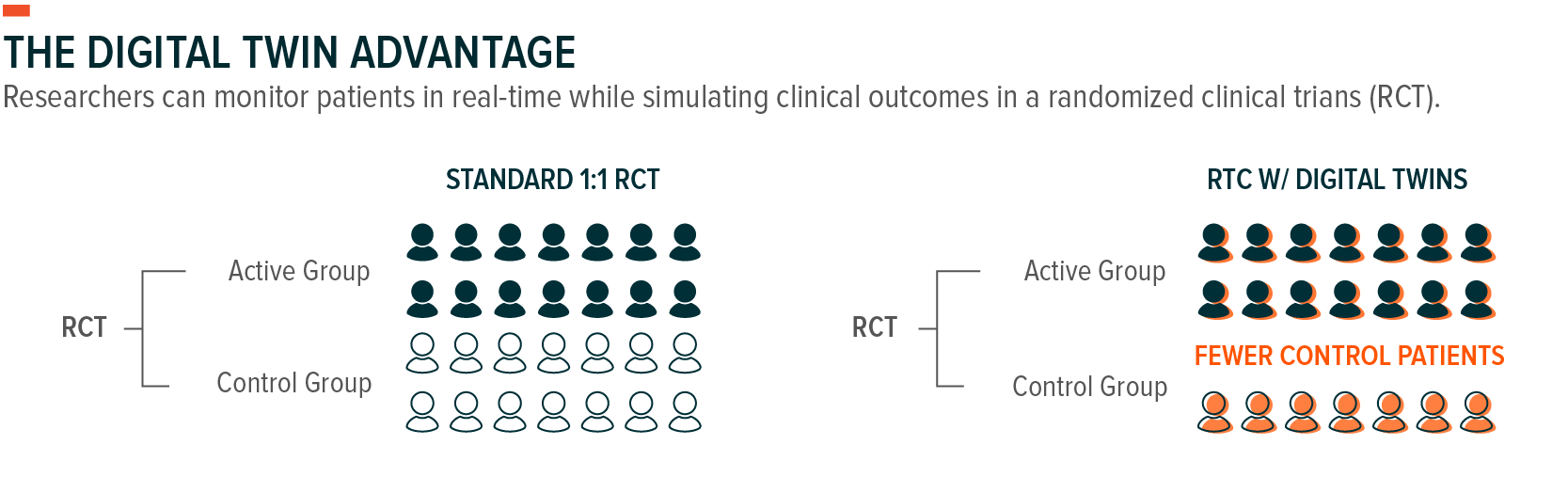
Clinical trials can also benefit from digital twins. These are AI-generated virtual models of real patients, simulating different dosing regiments and patient progressions. Although their impact can be significant, digital twins can reduce the size of the control group for clinical trials by 30%, meaning a greater proportion of clinical trial participants could receive the active ingredient versus placebo.16
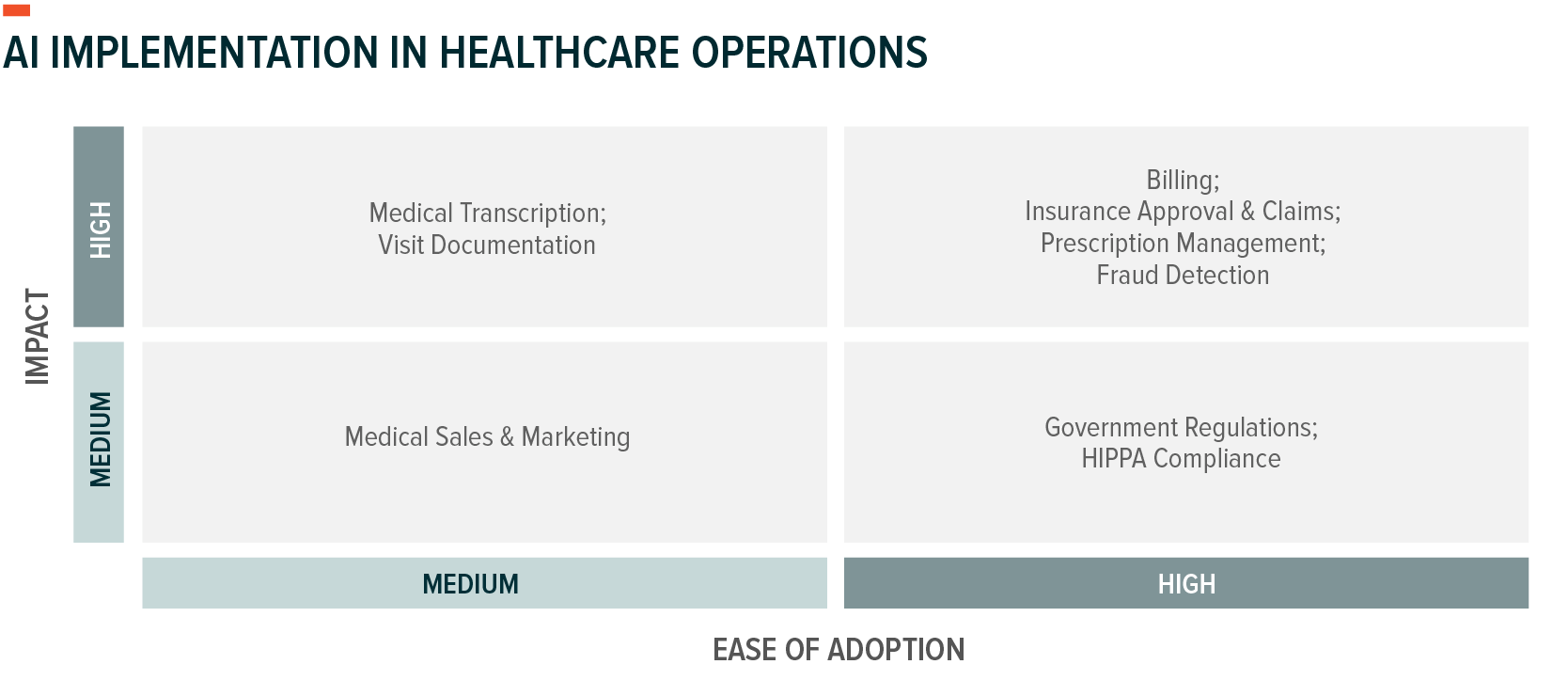
AI in Healthcare Operations: The Missing Link to Transformative Digitisation
Though healthcare has made great strides in digitising operations, an estimated 80% of U.S. healthcare documents are still sent via snail mail and fax.17 Documents in the industry are increasingly digital via electronic medical record (EMR) adoption, though the process remains inefficient and labour-intensive. Not surprisingly, 78% of physicians report health IT-related burnout and fatigue.18
AI can have widespread benefits in easing day-to-day tasks by healthcare providers, allowing them to spend more time treating patients. Among them, we view a select few having notable impacts:
- Extracting relevant information from medical records to drive medical decisions
- Assisting in notes, such as progress notes and discharge summaries, for EMR integration
- Providing care instructions to patients, like dietary restrictions prior to surgery
- Reducing the burden of obtaining pre-authorisation and submitting insurance claims
- Summarising medical journal articles
- Writing patient referrals, transfers, prescriptions, planning medically tailored meals, and scheduling visits
Across all day-to-day applications, AI can bring significant cost savings across the healthcare ecosystem:
- Private insurance firms could save 7–9% of their total costs, amounting to US$80–110 billion in annual savings within the next five years.19
- Physician groups could save 3–8% of costs, amounting to US$20–60 billion in savings.20
- Hospitals could save 4–11% of costs, amounting to US$60–120 billion each year.21
Automating Medical Record Documentation: Freeing Up Doctors’ Time
Physicians spend an estimated 39% of their time documenting patient information in electronic medical records.22 To help physicians free up time for patient care, multiple digital health companies have been prioritising the automation of patient records. Teladoc has notably partnered with Microsoft’s Nuance, an AI solution that automatically transcribes patient visits, saving an average of seven minutes per appointment. Nuance has seen a 70% reduction in the feeling of burnout from participating physicians.23
Seeing as turnaround times for traditional transcription services can be upwards of 72 hours, we’ve seen other tech giants enter the space.24 Amazon Web Services recently launched a new service, HealthScribe, for speech recognition, machine learning, and AI to summarise doctors’ visits.25 OpenAI, the company that developed ChatGPT, has also entered the space. In collaboration with Hint Health, OpenAI is working on new capabilities to allow doctors to record appointments and automatically transcribe visit notes.26
AI-Powered Chatbots: Facilitating Patient Care
We’ve also seen conversational AI tools tailored for the healthcare industry hit the market in hopes of simplifying the complex nature of healthcare, primarily achieving insurance coverage. Prior authorisation is a notably arduous process, in which insurance companies review and approve certain medical services or products prior to being rendered. This process can be time consuming, though new AI services can help reduce costs by 70%, from US$10 per transaction to US$3.27
Conversational AI tools allow physicians to input information in their own words and the service handles the rest. Digital health firm Doximity recently came out with DocsGPT, an AI-powered chatbot tool that facilitates prior authorisation, insurance claims, and patient communication. Once the doctor approves the AI-generated message, the platform also automatically sends it to the corresponding party. Recent studies have shown that when physicians utilise AI-based chatbots, responses are typically longer, higher in quality, and more empathetic, improving overall bedside manner.28
Conclusion
It is still early days for investors to quantify the impact of artificial intelligence, though the potential use cases for AI healthcare promise to revolutionise the entire industry. That said, picking individual winners in a field as vast as healthcare, which encompasses everything from drug discovery to insurance to treatments and beyond, can be challenging. ETFs can provide broad exposure to this megatrend, whether investors want to focus on digital health, genomics, or more pure-play AI.
Related Funds
CURE: The Global X S&P Biotech ETF (CURE) invests in companies at the fore of healthcare innovation and genomic science, including those involved in gene editing, genomic sequencing, genetic medicine and therapy, computational genomics, and biotechnology.
ROBO: The Global X ROBO Global Robotics & Automation ETF (ROBO) invests in robotics and artificial intelligence companies, including those involved with industrial robotics and automation, non-industrial robots, and autonomous vehicles.